Using The CSS position property You have to control how elements behave and are positioned on the page.There are 5 types of position
CSS Position Types
- Static Position
- Relative Position
- Absolute Position
- Fixed Position
- Sticky Position
Position Static:
It is a default position of every HTML element . This means if you don’t declare position for an element in CSS, it will automatically be set to static
 🙄🙄
🙄🙄
Position Relative :
The position relative remain in the normal flow of the document ,just like the static value. But now left/right/top/bottom will work.the values of (top, right, bottom, and left ) does not affect the position of any other elements . The positional properties to push the element from the original position in that direction which you set.
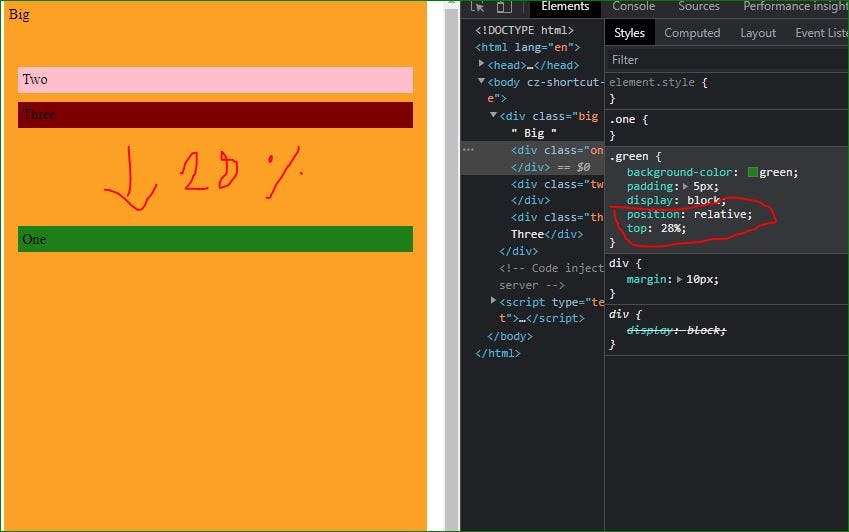
E.g: The green box moves down 28% of its parent element
Position Absolute :
The position absolute is positioned relative to their parent elements .If, the parent element has no Position Relative property in that case , The Child elements are moved from window relative.
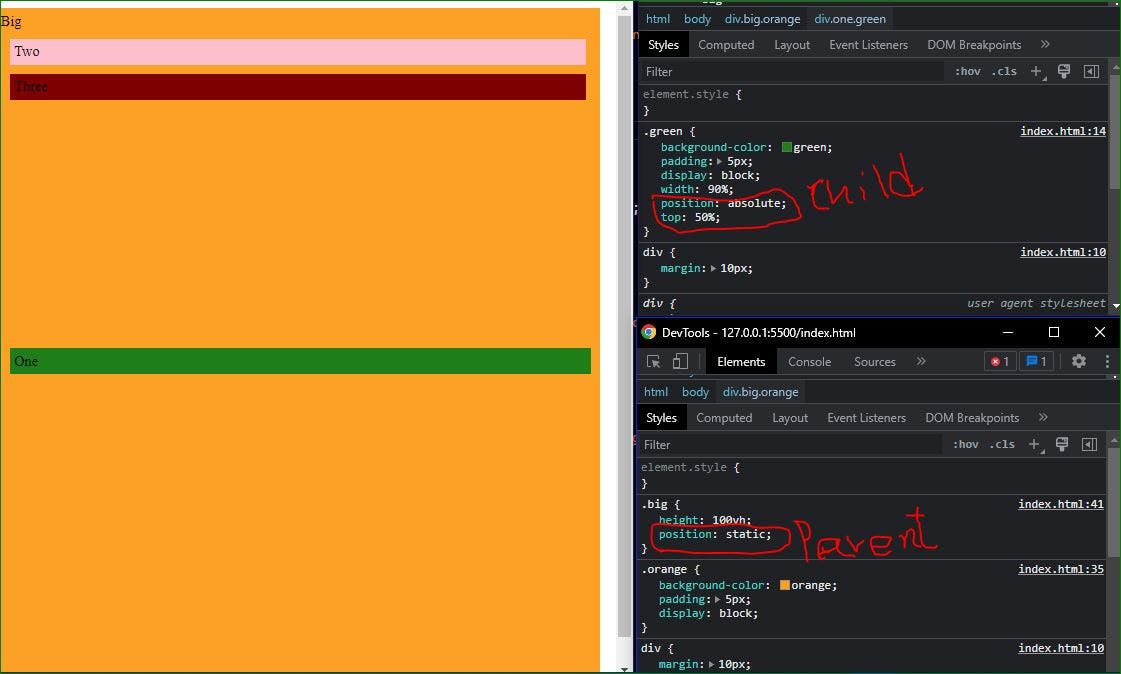 Parent element (.big) has no relative position so , the child element moved from window relative.
Parent element (.big) has no relative position so , the child element moved from window relative.
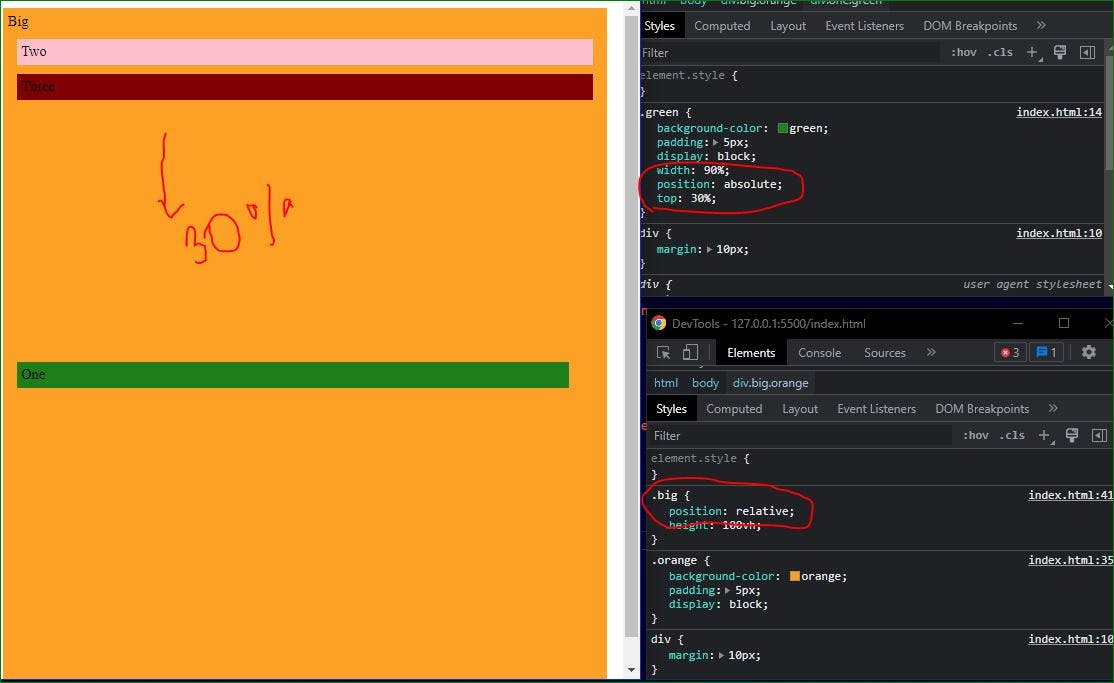
This case Parent element (.big) has relative position so , the child element moved from parent element relative.
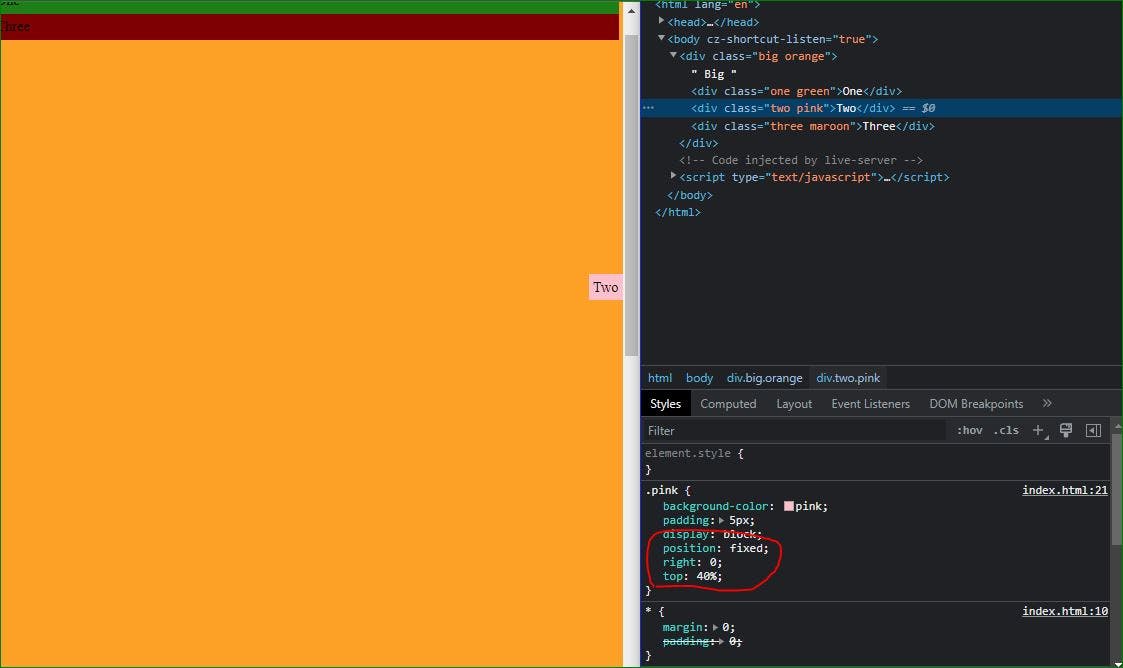
Fixed Position:
Position absolue and Fixed almost same . Difference just, unaffected by scrolling🤔 .
For example: Suppose, One element has position fixed property then the element fixed there event after scrolling.. 😀
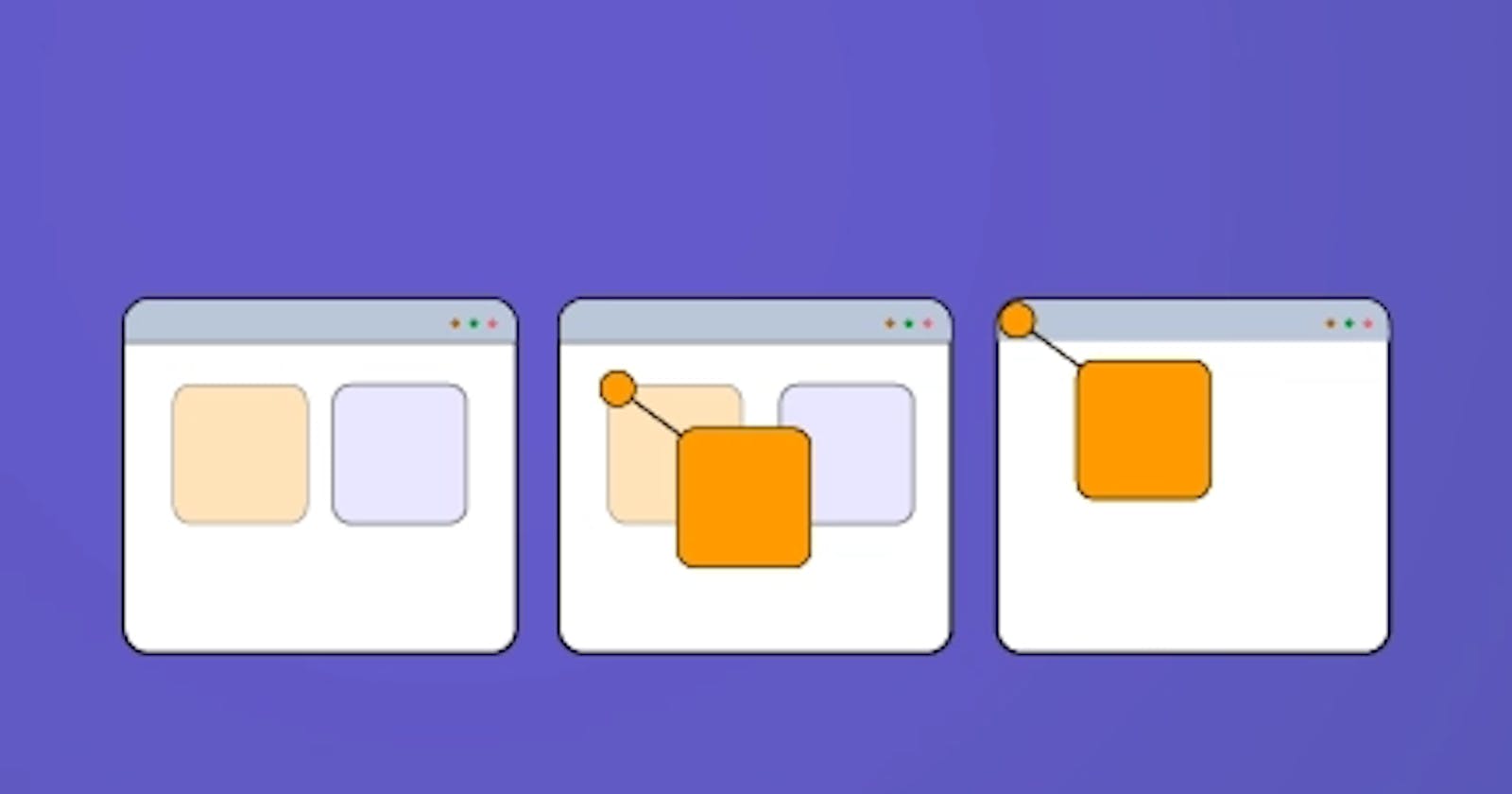
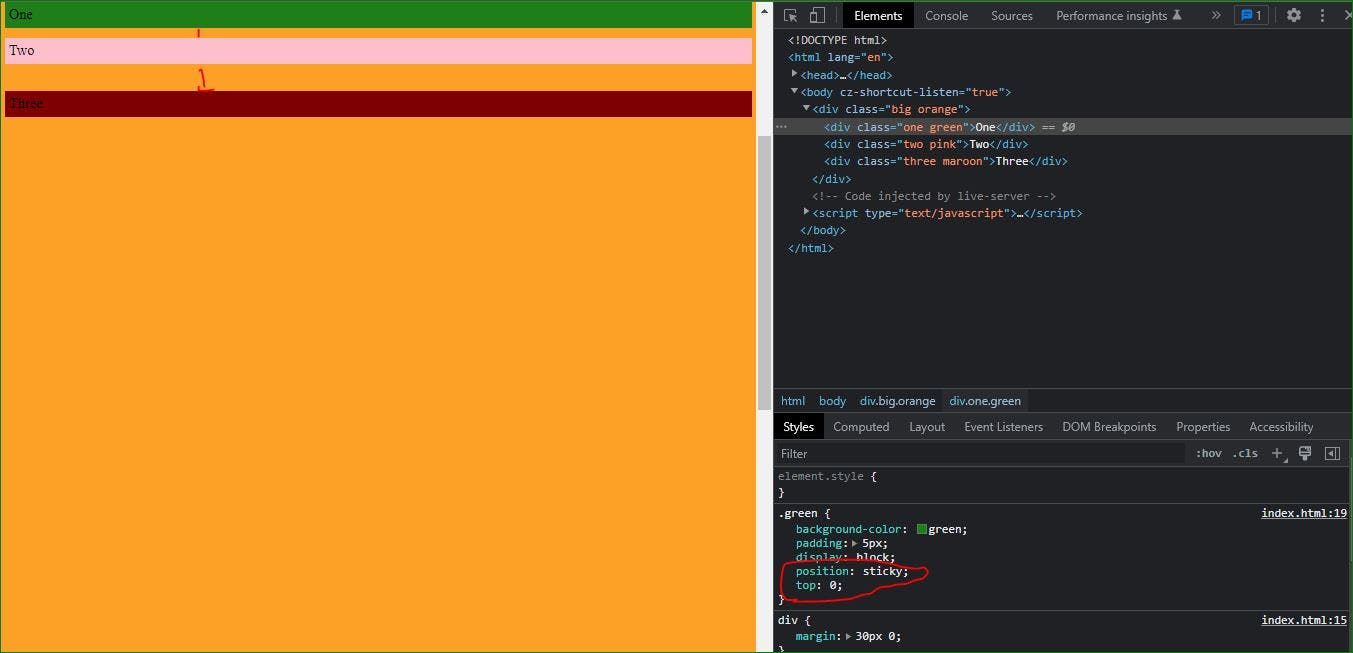
Sticky Position:
Sticky is little tricky 😄. The element(Fixed) behave normally but after scrolling when the set position match then the element fixed there. It is almost mix ofposition: relative and position: fixed